
 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE
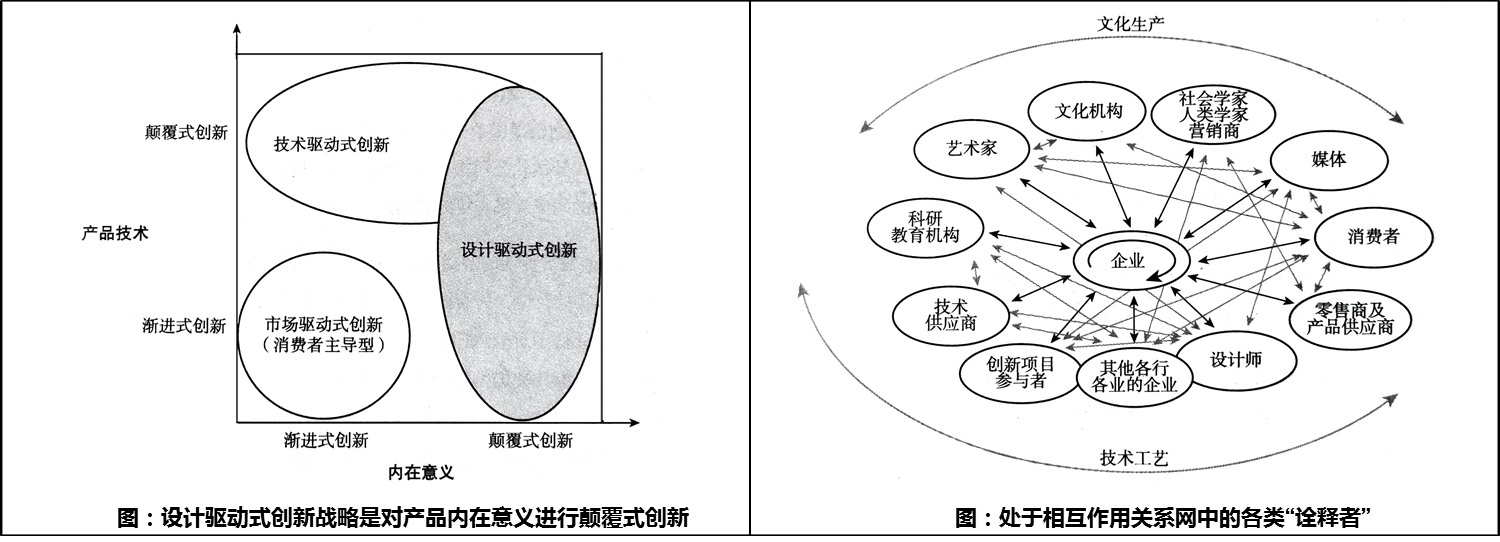
Traditional product design only focuses on the product itself, with little or no consideration for the ecological and environmental issues related to the product. Modern industrial ecology advocates that ecological and environmental issues should be considered together with other factors in the process of product development and design, so that products can meet demand and have good ecological and environmental performance. In real business operations, products are connected to the ecological environment in their own way, from the selection and acquisition of raw materials, manufacturing, packaging and transportation, installation and use, to disposal and recycling after scrapping. They consume resources and energy, emit pollutants, and have an impact on the ecological environment. The magnitude of these impacts is directly related to the initial design of the product. Based on the above principles, many fields have changed their traditional design work ideas, gradually thinking about problems from a systematic and comprehensive perspective, linking environmental issues with every link involved in the product, analyzing and evaluating the resources, energy consumption, and possible environmental impacts of each link based on ecological design and life cycle, from "passive governance" to "active prevention" throughout the entire process, and ultimately seeking methods and approaches to prevent, reduce, and eliminate these potential environmental hazards.
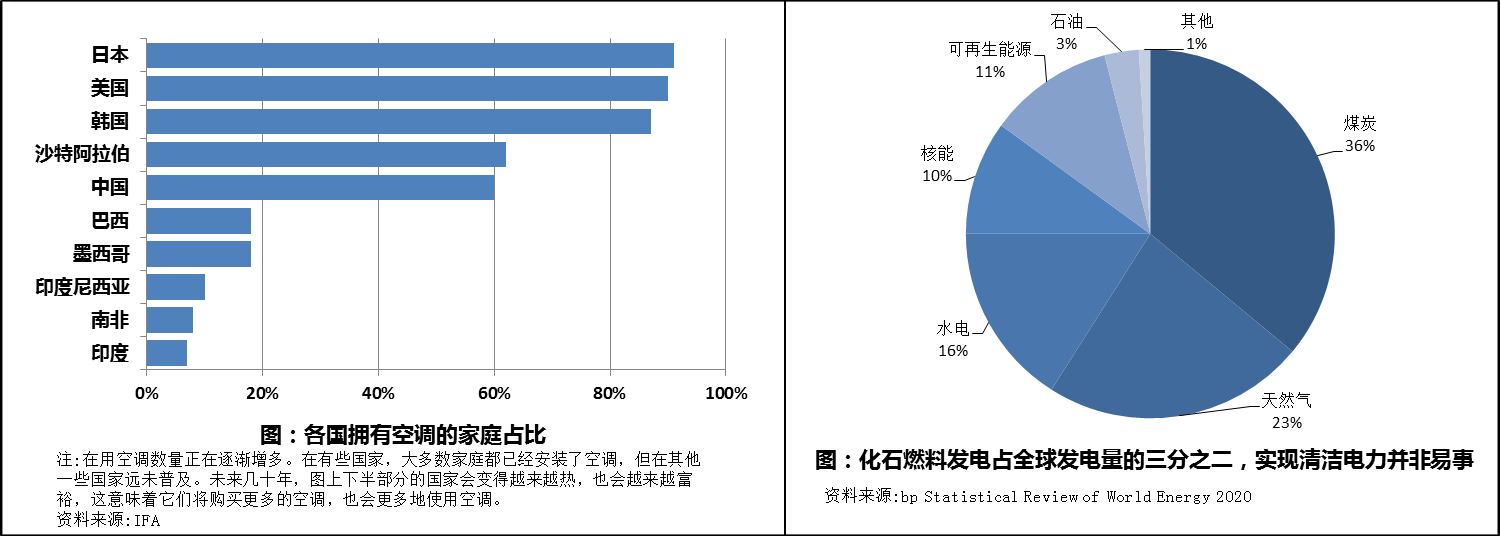
On October 8, 2024, the European Union's climate monitoring agency, the Copernicus Climate Change Service, announced that last month was the second hottest September on record globally, and overall, 2024 will be the hottest year on record. The report "Global Water Resources Status" coordinated by the World Meteorological Organization states that in the past five consecutive years, river flow has generally been below normal levels, and reservoir flow patterns are similar, which has reduced the available water for communities, agriculture, and ecosystems, exacerbating global water supply pressure. In 2023, global glacier mass loss reached its highest level in the past fifty years. Climate change is a common challenge facing human society in the 21st century, and every country has an inescapable responsibility in controlling carbon dioxide emissions. With global climate change, high temperatures and scorching heat are becoming increasingly frequent, and the number of abnormally hot days in summer is increasing every year. And in order to pursue a modern comfortable environment, households and businesses consume a large amount of energy in temperature regulation. In commercial buildings in the United States, energy used for space cooling accounts for 15% of energy consumption; The energy consumption used to meet residential thermal comfort in India accounts for 45% of residential energy consumption; In most parts of China, the cooling load of air conditioning exceeds 30% of the total load of the power grid. From 2007 to 2017, China added 350 million air conditioners domestically, making it the world's largest air conditioner market. Globally, air conditioner sales increased by 15% in 2018 alone, with a significant portion of the growth coming from four countries with particularly significant temperature increases: Brazil, India, Indonesia, and Mexico. It is expected that by 2050, the number of air conditioners in use worldwide will exceed 5 billion units. On the contrary, in order to survive in a constantly greenhouse changing world, our constant installation and use of air conditioning equipment may lead to further deterioration of the climate. Because air conditioning operates on electricity, the more air conditioners installed, the more electricity is required for their operation (electricity accounts for 99% of the energy used in space cooling systems worldwide). The International Energy Agency predicts that by 2050, the global demand for electricity for refrigeration will double. At that time, the electricity consumption of air conditioning worldwide will be equivalent to the total electricity consumption of China and India now.
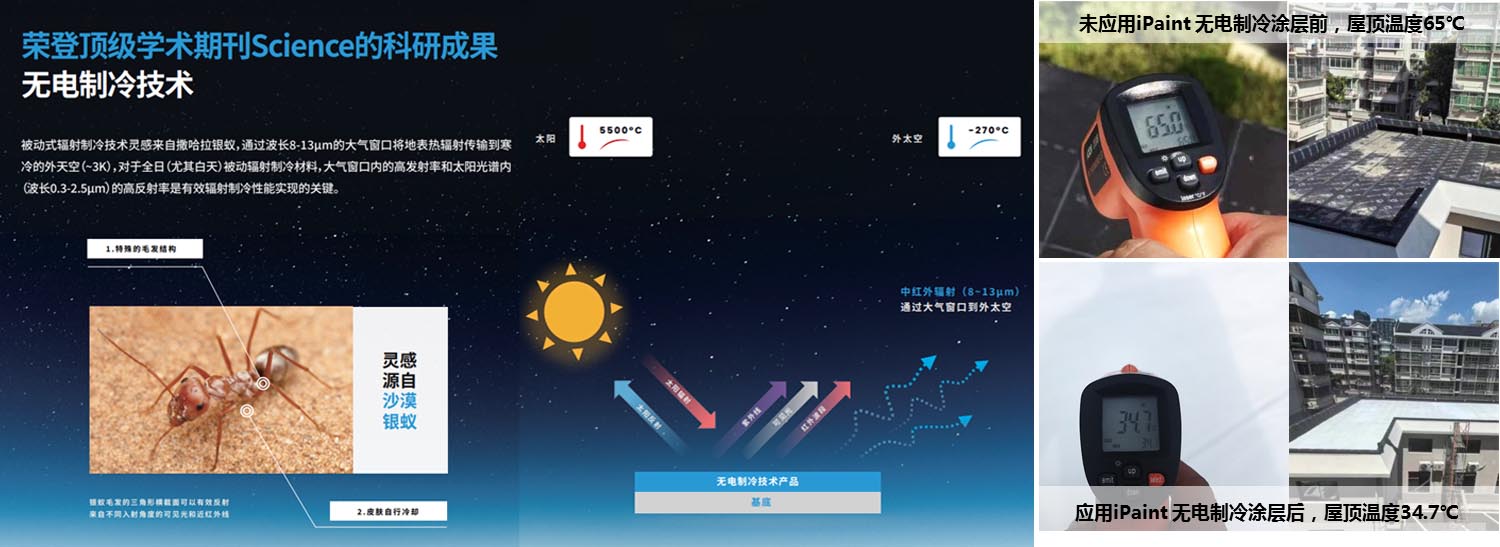
Due to the high dependence of air conditioning on electricity, reducing the electricity consumption of air conditioning can lead to a decrease in emissions caused by cooling. Therefore, on the path to achieving emission reduction targets, we must need innovative technologies, new business models, and new innovative production materials and processes. Ruiyan Technology New Materials has always been committed to sustainable development and is an advocate and practitioner of industrial ecology. In the field of electric refrigeration technology, REAL NEW METAL SCIENCE&TECHNOLOGY CO. LIMITED leverages Hong Kong's innovation advantages and collaborates with i2Cool to vigorously promote passive radiation refrigeration technology and products, providing comprehensive energy-saving refrigeration solutions for the construction of low-carbon cities and green communities

Currently, the challenge of global climate change is intensi...

MerRIND ® The Lean Lubrication brand was established in ...

In the long course of human civilization's evolution, we...
In the long river of human history, new technologies hav...

Hidden Champion "is a concept proposed by German busines...

On July 25, 2025, the Rhine River is rippling with blue ...

On July 12, 2025, the 2025 City Trip · Shanghai S...

MerRIND ® Lean Lubrication takes great pride in part...

Folding phone development trend: With its innovativ...

In today's world, technological progress and innovation ...