
 LANGUAGE
LANGUAGE
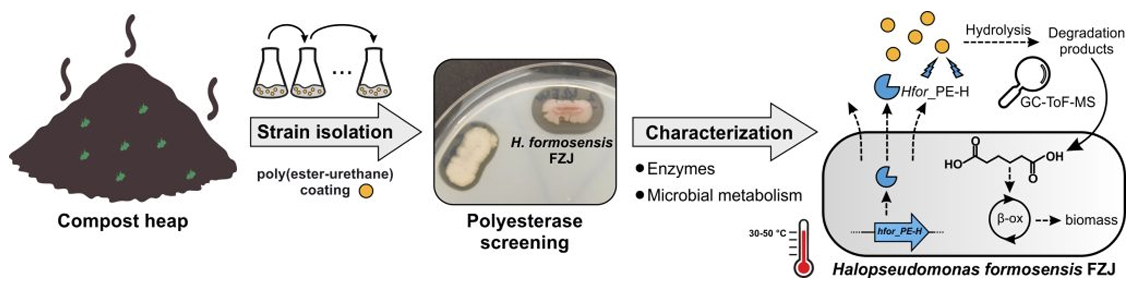
“Biodegradation of poly(ester-urethane) coatings by Halopseudomonas formosensis”
Plastic materials are indispensable in everyday life, they are inexpensive to produce and have many beneficial properties. But they are also a big problem because they accumulate in the environment, which has already led to global pollution. Although the term “plastic” is typically associated with things like bottles or bags, it is also widely used for the production of textiles, ropes, and fishing nets. The surfaces these materials are often coated with thin layers of polymers, e.g. so-called polyester polyurethanes, in order to improve and refine their properties. Such coatings, for instance, increase the durability of fishing nets, but they also make it even more difficult to break down or recycle these plastic materials.
One promising solution of this problem lies with microorganisms that are able to break down plastic and recycle its components. But which microorganisms can be used? Recently, bacteria of the genus Halopseudomonas have been discovered living in the deep sea, in sites contaminated with crude oil, or also simply in compost heaps. Researchers at HHU Düsseldorf and Forschungszentrum Jülich discovered that these bacteria have a particular appetite for coatings, and have published their results in two joint back-to-back articles in the journal Microbial Biotechnology.These publications thus provide detailed insights into the microbial degradation of plastics, underlining the importance of the newly isolated bacterium for future processes enabling plastic biodegradation and bio-upcycling. This work arose from a fruitful collaboration between the HHU Institute of Molecular Enzyme Technology IMET (funded by the BMBF projects NO-STRESS and PlastiSea) and the Jülich Institute of Bio- and Geosciences IBG-1 (funded by the EU Horizon 2020 project Glaukos). The coatings were provided by industry partners I-Coats and Covestro. The close collaboration between the IBG-1 and IMET teams with industry partners thus paves the way for potential applications in biotechnology and bioremediation.

当前,全球气候变化挑战加剧,绿色低碳转型已成为人类可持续发展的必由之路。中国作为全球最大的发展中国...

默芮达®精益润滑品牌成立于2008年,是一家创新型的专业润滑油与新材料工业企业,企业秉承“创业、创新、创造...

在人类文明漫长的演进历程中,我们正站在前所为有的关键节点。每一次重大变革,都有能源的开发与利用紧密相连。面对全球气...
在人类历史的长河中,新技术始终是推动社会变革和进步的核心力量。从工业革命时期的蒸汽机、电力技术,到如今的人工智能、...

“隐形冠军”(Hidden Champion)是德国企业管理学者赫尔曼·西蒙1990年提出的概念,专指市场地位位列...

2025年7月25日,莱茵河边碧波荡漾,绿茵满堤,鹭鸟栖息,鱼翔浅底,万类夏日竞自由!华东理工大学作为以化工特色闻...

2025年7月12日,由香港城市大学研究生会(CUPA)主办的2025城市行·上海站活动于上海举行...

默芮达®精益润滑荣幸参与由香港城市大学主导的国际合作项目“创新驱动可持续未来:先导计划(F...

折叠OCA是一种用于折叠手机屏的透明光学元件的特种粘胶剂,在折叠手机屏幕的盖板层、偏光片层、触控膜层、OLED层间...

当今世界,技术进步和革新已经成为推动制造业持续发展的核心动力。作为全球经济的重要支柱,制造业在采用新技术、提高生产...